TDX 2025 - Day 2 (Part 2)
Second batch of notes from the second day of Trailblazer DX, the yearly Salesforce developer conference. My notes from day one can be found here and here.
Similar to my notes from day 1, I’ve split my notes from day 2 out into a couple of pages for length. The first batch of notes can be found here.
Deep Dive on Advanced Prompt Engineering
Intro
- LLMs & Agents

- LLMs are really sophisticated pattern matching systems
- LLMs by themselves are limited in terms of what you can do with it, especially from a business value perspective
- LLM Optimization Journey Steps (not mutually exclusive, often used in tandem)
- Prompt Engineering - Logical first step to get started with an LLM
- RAG - Solve complex use cases with knowledge augmentation
- Fine Tuning - Train LLM for domain-specific use cases
- Model Distillation - Transfer large LLM knowledge to smaller LLM
Prompt Basics
- Why do prompt engineering?
- LLM with vast general knowledge, lacks context for enterprise adoption
- Challenges with Agentic systems to follow instruction & provide expected responses
- Prompt engineering is the easiest way to guide and control LLM text gen
- Solve NLP tasks, content gen, machine translation, agentic system, etc…

- LLM Context Window: Amount of information the model can lookup during prompt execution
- Limited memory
- In Context Learning (ICL): Ability of model to gain short term insights from instructions, examples, and context provided
- This is often provided in a long prompt, via system instructions, examples, specific data format that you’re looking for
- See the next section for recommended prompt elements
Prompt Elements

- Use the following to try and get more deterministic output from a very non-deterministic system
- System Instructions
- Context, History, Examples
- Validations
- Make sure to include at least one, but more for COT
- Input Data
- Response Format
- Questions / Ask
- Remember that prompt formatting is critical
Advanced Prompting Techniques
- Few Shot Prompting: Teaching LLMs new concepts / patterns in the moment (ICL) through examples to improve model prediction accuracy
- Isn’t necessarily the best for complex, step-by-step thinking
- Chain of Thought (COT): Thinking step-by-step
- Use this for complex reasoning
- Include in your prompt: “Please explain your reasoning steps.”
- Complex arithmetic or logical problem solving, requires step-by-step reasoning to get accurate result
- Few examples with step-by-step reason will help the model learn (ICL) and solve similar problems
- Include longer lists of validation steps in your prompt
- Example: Matching of invoices to order data
- Prompt Chaining: Orchestration using prompts and speciality models
- Decomposing complex tasks into multiple prompts (sub-tasks)
- Solving with speciality models, chaining them together to build complex workflows
- Example: Build an Invoice Agent
Slack + AI
- 3 primary ways you can get AI in Slack
- Slack AI
- Agentforce in Slack
- Third Party Agents / AI Providers
- Focused on the following principles
- Guided experience instead of open-ended experience
- Company knowledge instead of just public knowledge
- Self-hosted models vs. 3rd party hosted models
- Slack AI aspects
- Enterprise Search - just launched yesterday
- Clear, concise answers based on conversations, data, and apps
- Conversation Summaries
- Catch up on channels and threads in one click
- Recaps
- Get daily digest of what’s happening across your teams
- Huddle Notes
- Capture key takeaways and action items from your huddle
- Enterprise Search - just launched yesterday
Developer Experience Roadmap
Agentforce for Developers: Dev Assistant
- Inside of the VS Code Salesforce Expanded Extension Pack
- Free for all orgs
- Dev Assistant should be grounded in your org’s specific data model, just make sure that you run the
Refresh SObject Definitionscommand before starting. - You can use
/commands in the chat interface like/explain,/test, and/document - Can be used to generate tests
- Can be used to generate code in LWC or Apex
- In my opinion, it appears probably still not as helpful as Cline or Github Copilot
Code Analyzer
- Can access via separate CLI tool or as a VS Code extension
- If you use VS Code, make sure to enable Code Analyzer 5 via the VS Code settings
- CLI command:
sf code-analyzer run
- Includes a “QuickFix using Agentforce” when using the VS Code extension
Apex REST API Enhancements
- You can generate OpenAPI Specs (OAS, formerly Swagger) for Apex REST APIs
- Right click on class and select the “Create OpenAPI…” option
- Generates the
yamlfile
- Apex API Endpoints are now visible in the
Setup > API Catalog > Apex
Hot Module Reloading for LWC
- CLI command:
sf lightning dev app - Enables “local development” in org, which auto-refreshes LWCs as you make changes
Scale Products
- Products integrated into DX experience to help better diagnose performance and scaling issues
- Available today in Sandboxes or Production
- All available under
Setup > Scale
- All available under
- Products:
- Scale Test - Suite of products and reports
- Test Plan Creation
- Shows when peak usage times are over the past month
- Shows Most used and slowest pages, and what LWCs are the most used and slowest
- Shows Server Side traffic and triggers
- Overall, shows tons of telemetry on the platform for usage
- Test Scheduler
- Test Execution
- View results of tests, compare across multiple test runs to identify issues
- Test Plan Creation
- Scale Center
- Observability data
- Can go back up to 30 days in Sandbox or Prod
- Shows snapshots of different errors
- Performance Analysis: Can also allow you to start various different analyses directly in Setup. Things like:
- Apex Concurrency
- Row Locks insights
- Database Performance
- SOQL optimization
- ApexGuru Insights <--- Great place for OA team to review!!
- Code recommendations
- SOQL/DML Analysis
- Expensive Methods
- Unused classes & methods <----- AWESOME!!
- Scale Test - Suite of products and reports
Roadmap


Build Headless Agents with the Agentforce API
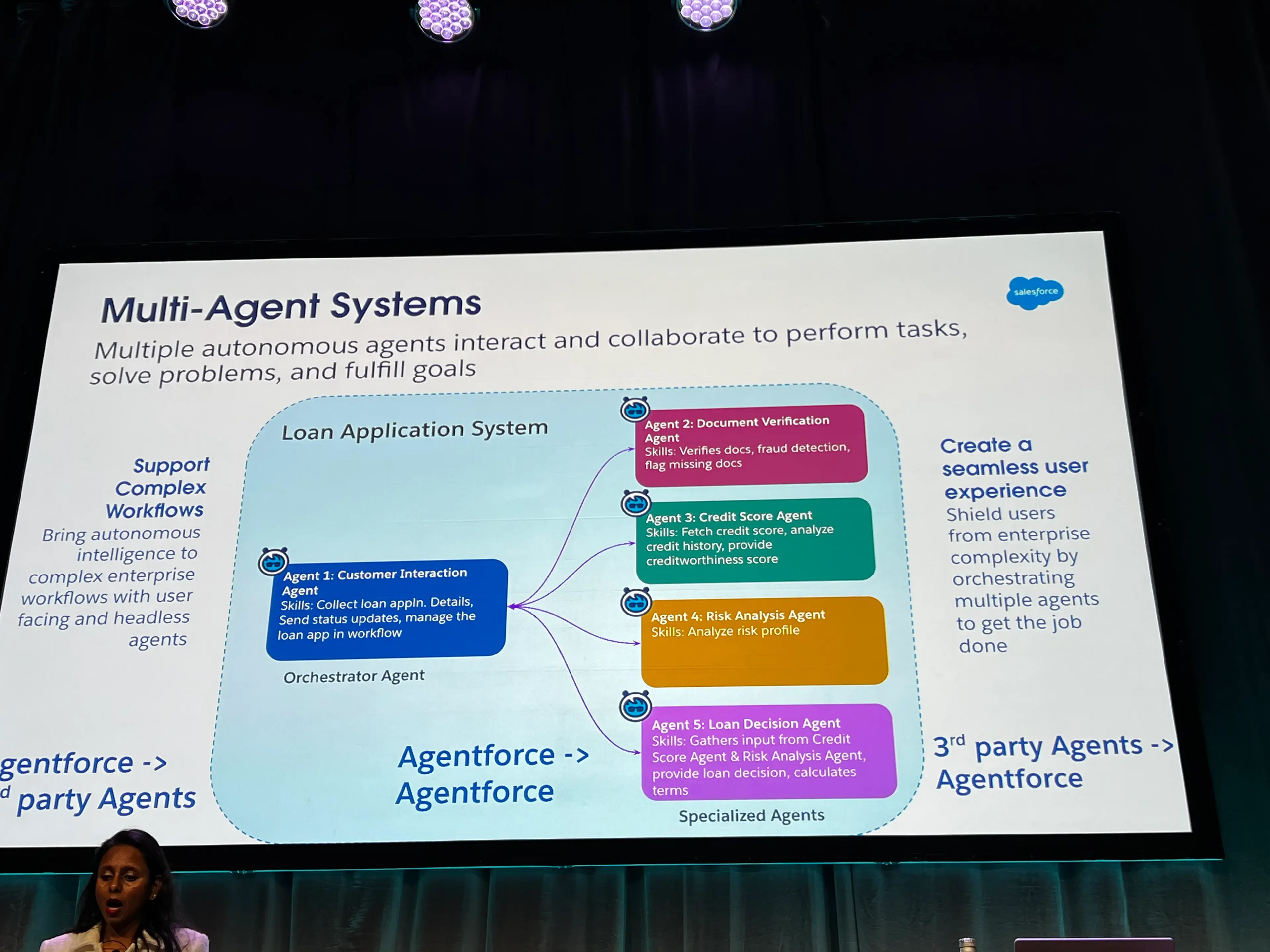
- Headless Agents: Intelligent, autonomous systems that operate in backend to automate routine tasks, enhance personalization, and scale operations.

- Multi-Agent Systems: Multiple, autonomous agents interact and collaborate to perform tasks, solve problems, and fulfill goals
- Agents will need to be able to communicate with each other, including Agentforce to 3rd party agents, and vice versa
- Agentforce API can now allow 3rd parties reaching in to communicate with Agentforce
- Agents will need to be able to communicate with each other, including Agentforce to 3rd party agents, and vice versa
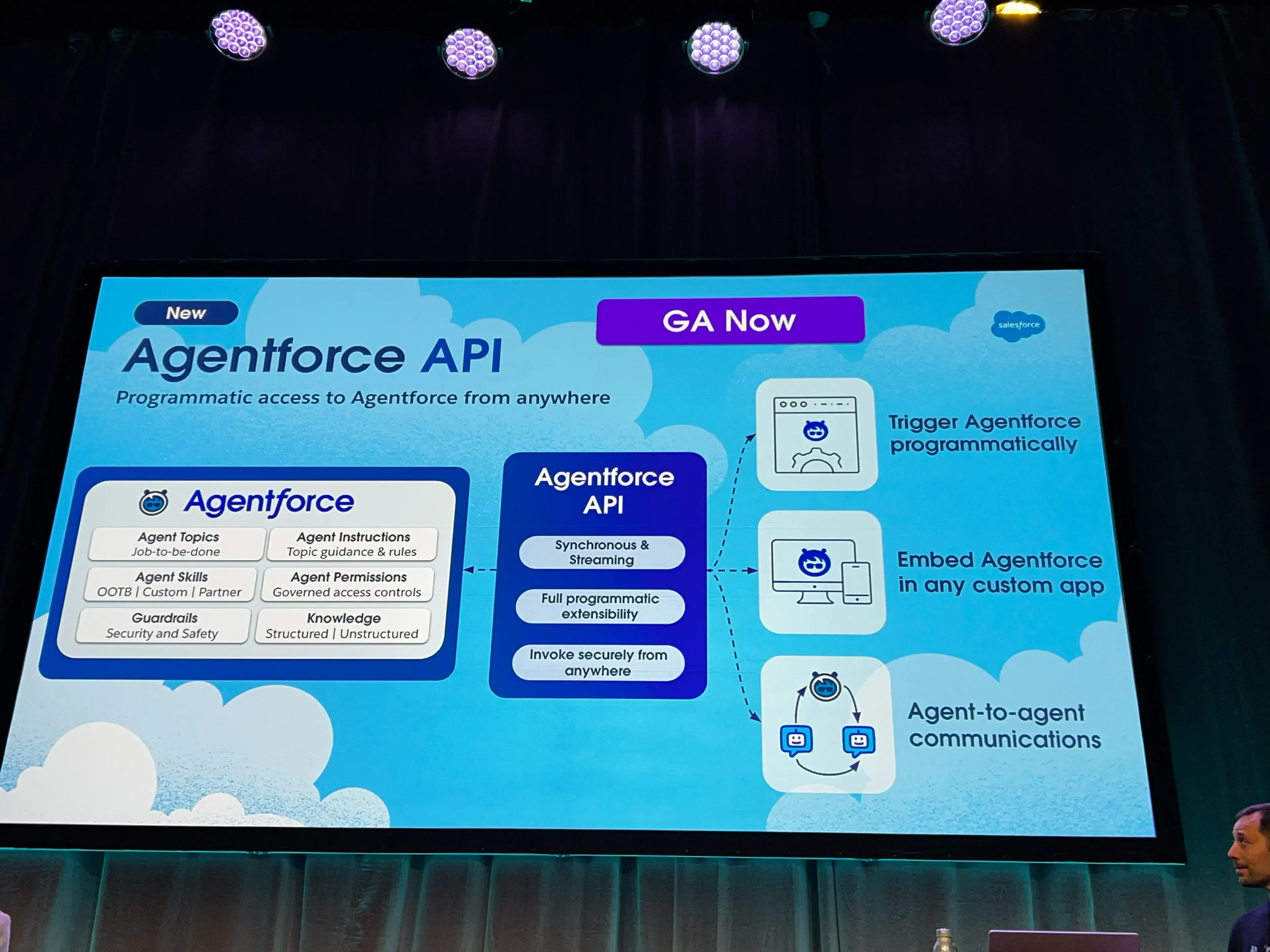
- Agentforce API Overview
- REST API
- 2 modes:
- Synchronous Mode
- Single, blocking HTTP request
- Pros: Simple to implement, good for server-to-server comms
- Cons: No UI feedback while the user waits for a response
- Asynchronous
- Server-sent events
- Con: More complex implementation
- Pro: Dynamic UI feedback thanks to streamed events and chunking
- Synchronous Mode
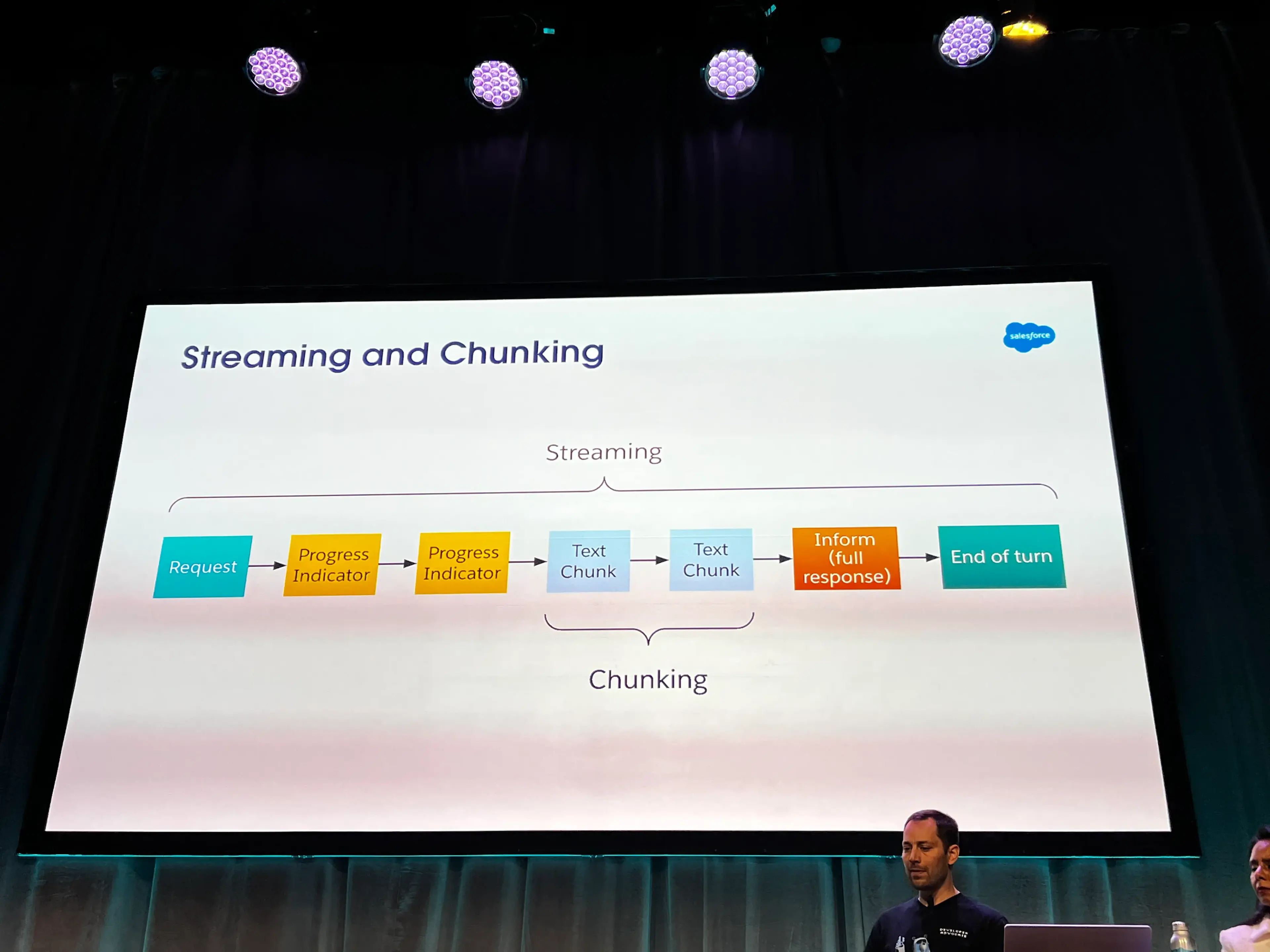
- Streaming and Chunking
APIs to Communicate with Agentforce

- 2 APIs that can interact with Agents
- Messaging for In-App & Web (MIAW) - Human friendly
- Agent API - Lighter weight setup
- Steps for Setup
- Create connected app
- Required scopes:
chatbot services,salesforce api
- Required scopes:
- Add connected app to the Service Agent Configuration
- Create connected app
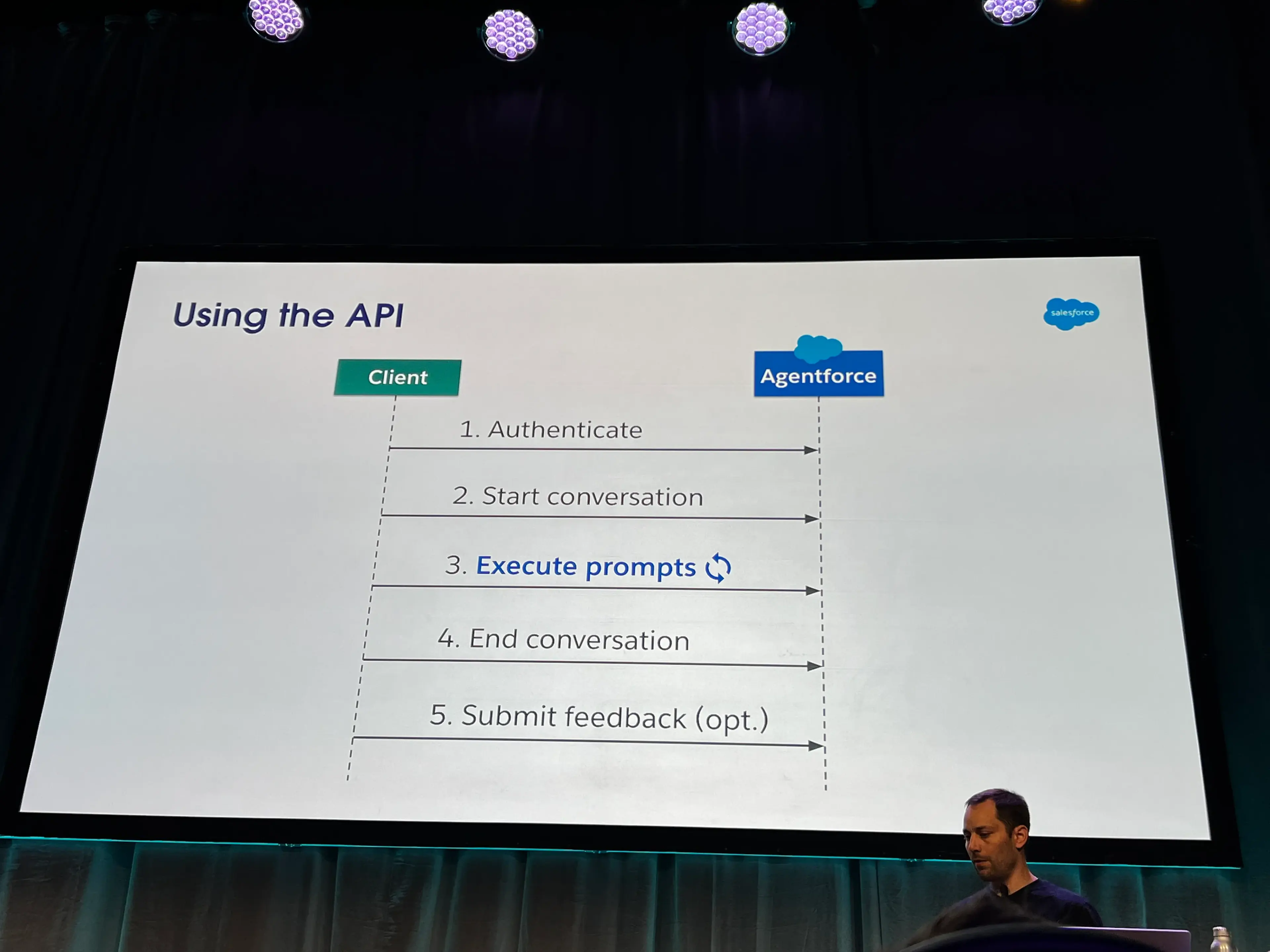
- Using the API
Demo & Examples
- Agent API Postman collection can be cloned and forked
- Example: User navigates to a webpage, you gather info and fire off a request to a middleman server (Node server, for example) that then sends some specific queries / requests to Agentforce, and start streaming back things like recommendations or other results