Einstein Copilot
Primary Pillars of Einstein Copilot
- Prompts
- Actions
- Dynamic Plans
Architecture of Einstein Copilot
Layers to Copilot
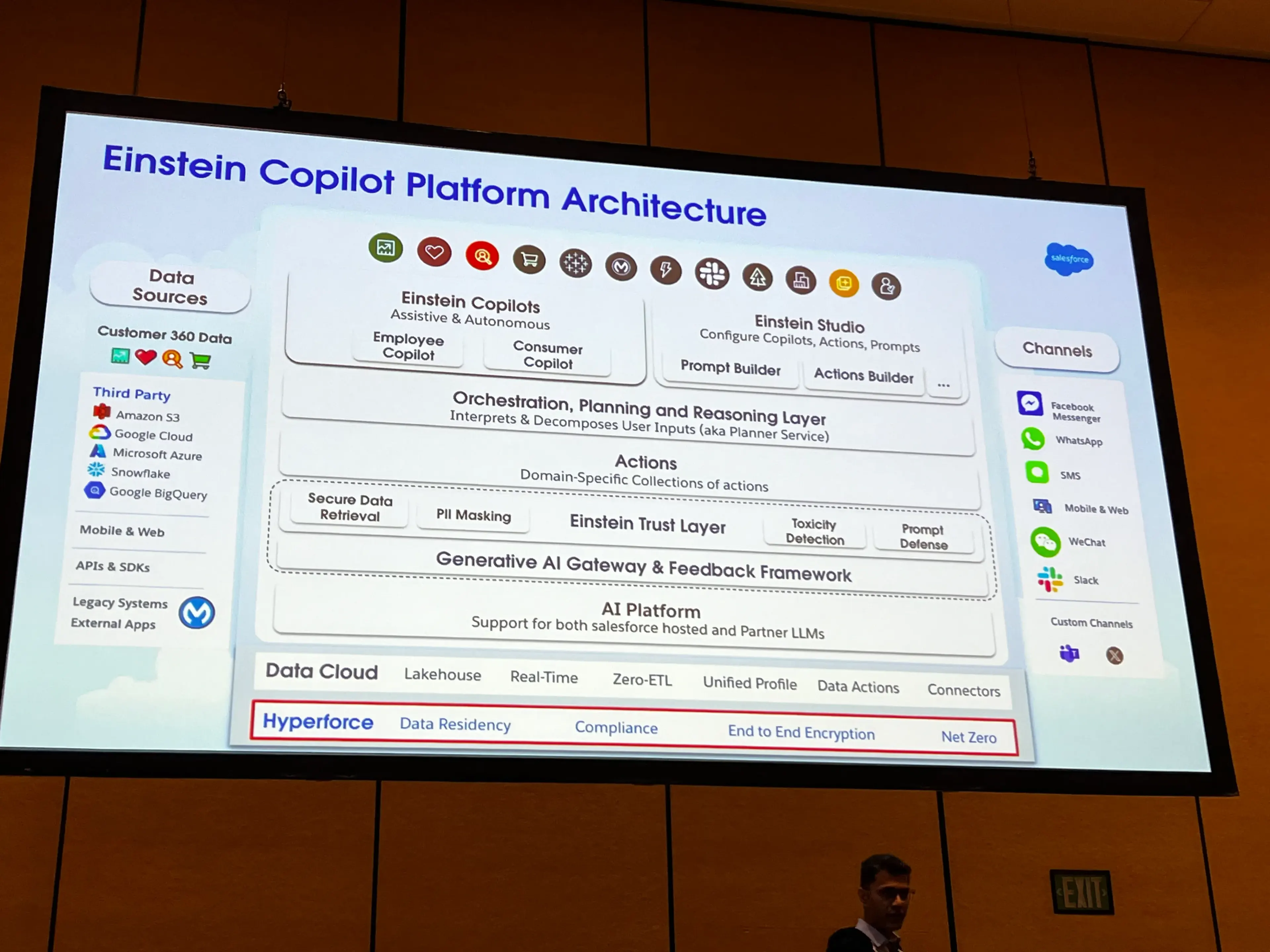
- Infrastructure: built on Hyperforce
- Data layer: Data Cloud
- Allows for pretty nice disambiguation
- AI Platform: Using Salesforce-hosted or partner-hosted LLMs
- Foundational Services Layer:
- Gen AI Gateway: Provides single abstraction on top of various LLMs
- Feedback Framework: Stores feedback into Data Cloud
- Einstein Trust Layer: PII Masking, Secure Data Retrieval, Toxicity detection, and prompt defense
- Actions
- SFDC will provide a lot of OOTB actions
- Partners, ISVs, and devs can create custom Actions
- Include
- Orchestration, planning, and Reasoning Layer
- Where LLMs and Actions meet
- Generates dynamic plans
- Executes in the User context, not the system context
- Einstein Studio
- Low- & No-code
- Build actions
- Configuring the copilots themselves
- Einstein Copilot: The actual chat interface with the AI
- Could include many different channels, including messaging apps off-platform
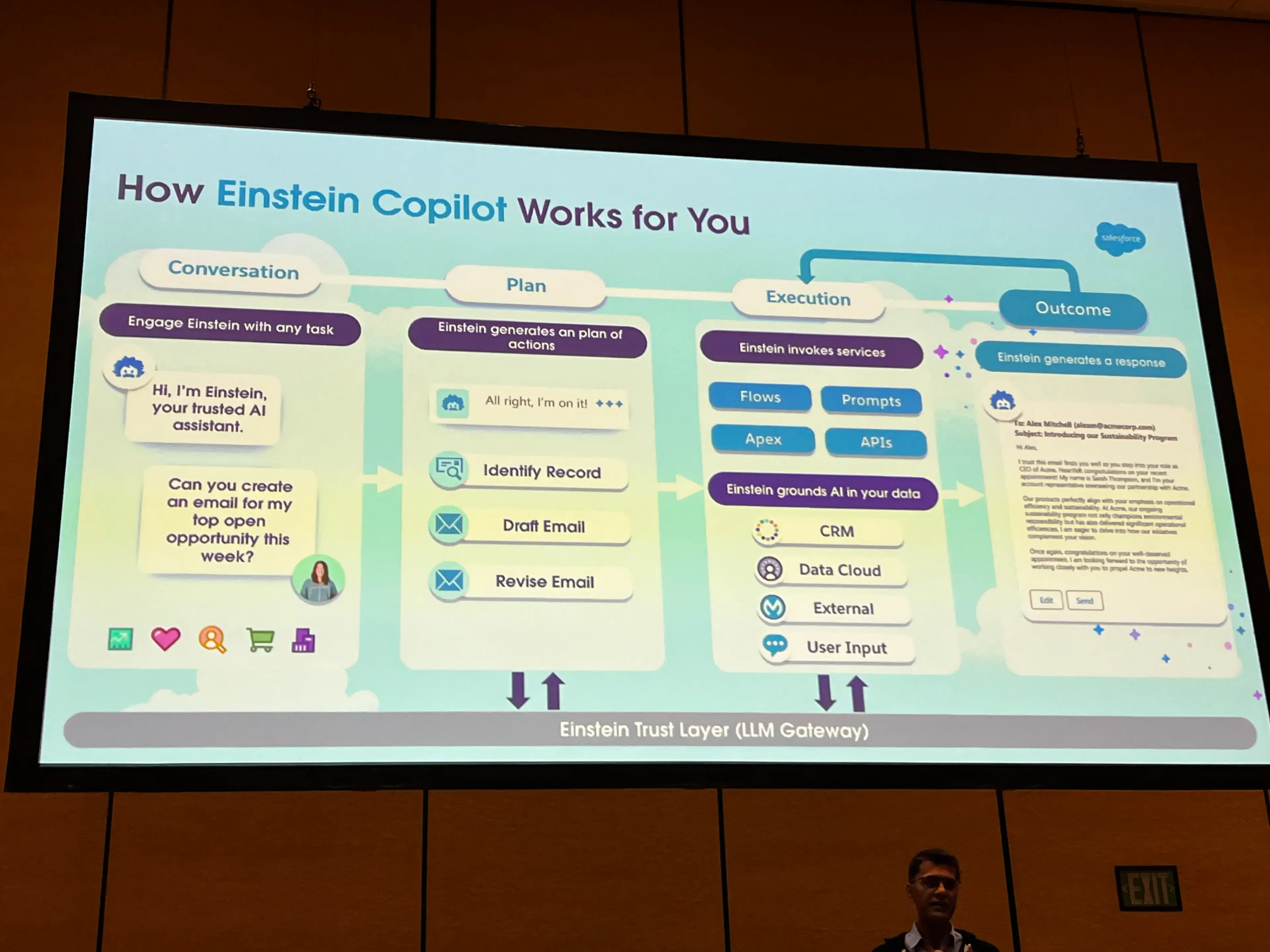
How Copilot Works
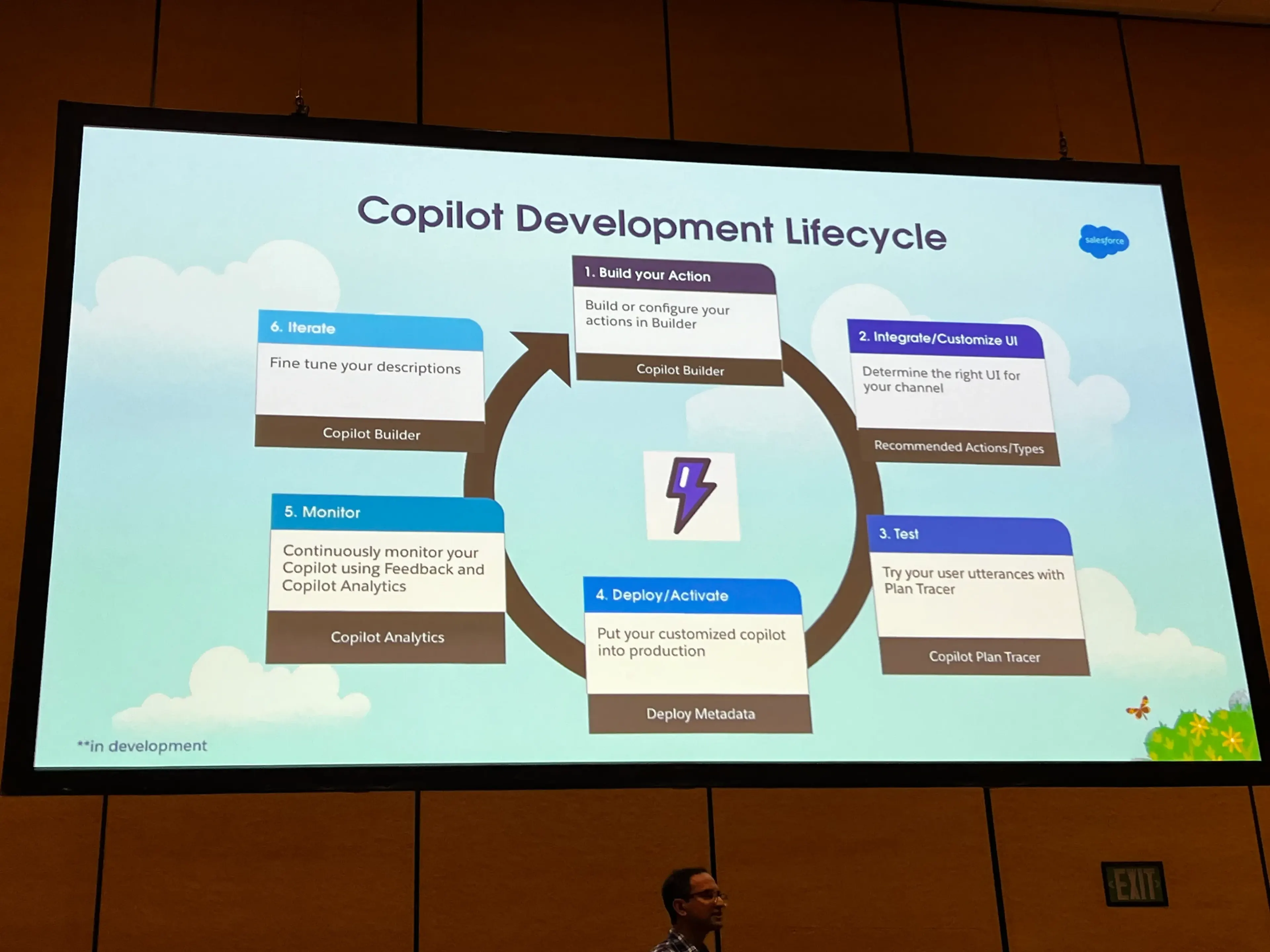
Developing and Deploying Copilot
Customizing Copilot
- Copilot Builder: Where you build and customize your Actions
- Salesforce shipping a number of general and domain/cloud-specific actions
- You can build your own too though external services / MuleSoft APIs, flows, and Apex
- You can also test your copilot here, to inspect the dynamic plans that are generated based on Actions and prompts
- Experience Type System: What you use to customize UI for Copilot
- You can customize branding, or rendering on different channels
- You can also have recommended or suggested actions based on the context of where the User is in Salesforce

- Copilot Analytics: Observability for usage of copilots
- Can include feedback and performance metrics
References



